Bone conduction hearing aids offer several advantages over traditional air conduction hearing aids in protecting hearing, primarily in the following aspects:
-
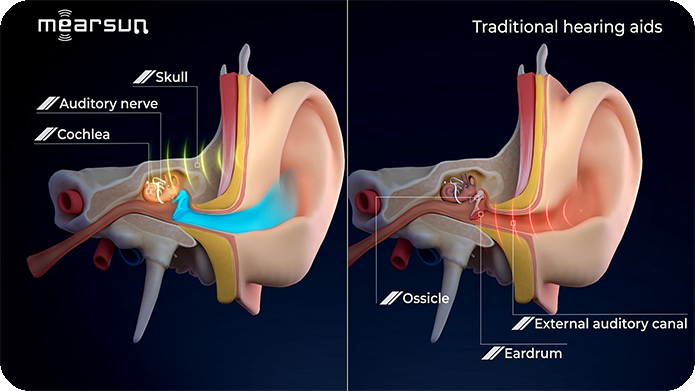
Reducing Cochlear Strain: Traditional air conduction hearing aids work by transmitting sound to the inner ear’s cochlea, creating auditory perception. Prolonged use at high volumes can exert additional pressure on the cochlea, potentially increasing the risk of hearing damage. Bone conduction hearing aids, on the other hand, transmit sound vibrations directly to the skull, which then conducts the sound to the inner ear. This method avoids direct stimulation of the cochlea, thereby reducing this risk.
-
Lowering Noise Exposure: Traditional air conduction hearing aids are susceptible to environmental noise. To hear clearly in noisy environments, users might increase the volume, thereby adding stress to their auditory system. Bone conduction hearing aids rely more on the bone conduction pathway for sound transmission, which means they impose less burden on the auditory system in noisy environments, offering more effective hearing protection.
-
Avoiding Ear Canal and Middle Ear Issues: Air conduction hearing aids transmit sound through the ear canal to the middle and inner ear. This process can sometimes lead to chronic ear canal and middle ear problems, such as earwax blockages and middle ear infections. Since bone conduction hearing aids do not depend on the ear canal and middle ear for sound transmission, they can help reduce these potential issues.
In summary, bone conduction hearing aids protect hearing more effectively than traditional air conduction hearing aids by reducing direct cochlear stimulation, lowering noise exposure, and avoiding ear canal and middle ear problems. These aids are particularly suitable for individuals who need to wear hearing aids for extended periods and wish to minimize the risk of hearing damage.

Share:
Bone Conduction Hearing Aids Optimize Residual Hearing for Mild to Moderate Hearing Loss